3 approaches to analysing stocks to trade markets your way
No investment plan or trading strategy is complete without a thorough analysis of markets to identify the opportunities and determine any potential risks.
Do-it-yourself (DIY) investors and traders need to research and analyse markets to understand the potential direction that global and local markets could move.
This process should start with a broader macro view, gained by studying the global and local dynamics that influence different economies and their currencies while leveraging different methods to analyse companies to gain a micro view.
These insights are important to formulate an appropriate strategy to position trades and right-size those positions by adjusting the size of a trade by either increasing or decreasing the number of shares or contracts held.
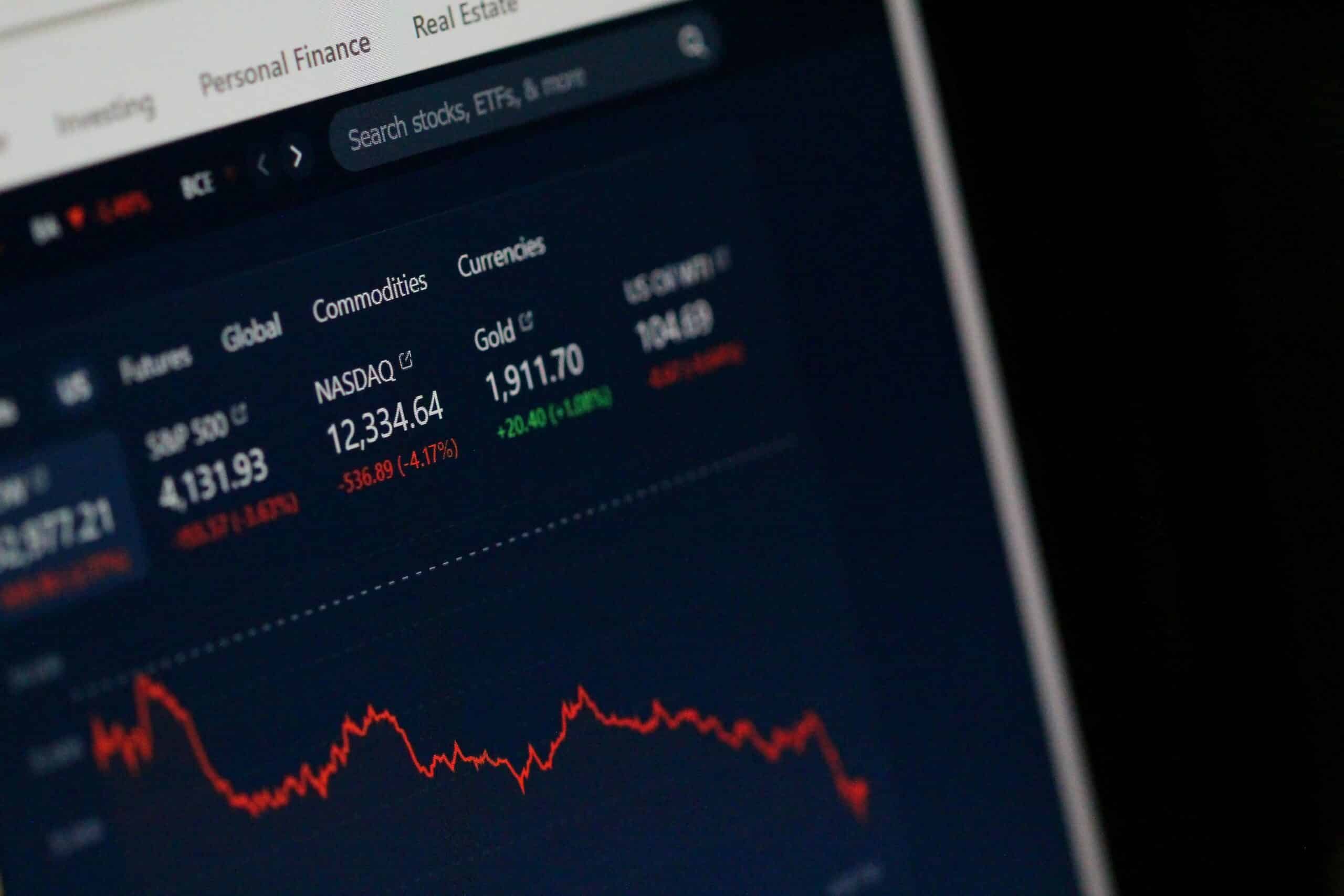
Traders and investors have various tools at their disposal to conduct this research, with the most prominent fundamental, technical, and sentiment analyses.
Fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on economic news, global events and company data to evaluate a company’s intrinsic value and understand how external and internal factors might impact stock prices.
Analysing stock picks using a fundamental analysis approach is typically associated with long-term investment strategies.
The key components of fundamental analysis may include the macro elements, using industry and economic analysis to better understand the company’s competitive landscape, growth prospects, and economic factors affecting the industry, alongside the overall economic environment, including factors such as interest rates, gross domestic product (GDP) growth, and inflation, among others.
From a specific company perspective, a comprehensive fundamental analysis should encompass financial information from available documents such as financial statements and annual reports.
These publicly available documents reveal factors such as a company’s historic profitability, its balance sheet, which demonstrates a company’s financial health at a specific point in time, and cash flow statement to understand elements such as liquidity, how much cash the company generates, and how the management team approaches debt management and capital raising approaches.
Additional elements to review could include a range of financial ratios, such as the profitability ratios to determine a company’s ability to generate profit, the liquidity ratios, which assess a company’s ability to meet its short-term financial obligations, and its solvency ratios to determine the company’s long-term financial stability.
Technical analysis
Technical analysis is a method of evaluating securities by analyzing statistical trends in price movements and trading volume using charts and historical data to identify trading patterns and predict future movements.
This approach typically forms the cornerstone for many CFD trading strategies as a technical analysis solely relies on price and volume data. In contrast, fundamental analysis focuses on a company’s financial health, which is more suited to long-term investors.
When diving into technical analysis, traders should understand important underlying principles, such as market efficiency, which assumes that all information is already reflected in the price and that price movements are influenced by supply and demand factors, which creates patterns.
Traders also use indicators when analysing stock pics from a technical perspective, which generate trading signals based on calculations that incorporate price and volume data. Popular indicators include:
- Moving Averages: Smoothed out price data used to identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements.
- Stochastic Oscillator: Shows the closing price’s position relative to a price range.
- Bollinger Bands: Measures market volatility and provide potential trading signals.
Additional technical analysis tools that traders can leverage include support and resistance levels, which are price levels where buying or selling pressure is expected to be strong, and chart patterns that provide a visual representation of price movements that can help predict future trends.
Sentiment analysis
A sentiment analysis gauges the overall attitude or mood of market participants towards a particular company stock based on market commentary and trading reports.
At its essence, sentiment analysis aims to determine the emotional tone behind words shared in news articles, financial reports, social media, and other forms of data. While it is a less-used tool, traders are increasingly harnessing it to gain an edge by potentially predicting market movements to inform their trades and adjust their positions accordingly.
For instance, a surge in positive sentiment for a particular tech stock might indicate a potential upward price movement or negative sentiment may indicate market or company volatility ahead.
Sentiment analysis can also help identify discrepancies between market sentiment and underlying fundamentals, with these market anomalies presenting potential trading opportunities to generate a return.
Sentiment analysis typically starts with data collection, where traders gather relevant information before sanitising the data by removing noise, stop words, and irrelevant information. They can then assign a sentiment score to the text, ranging from highly negative to highly positive. By recording these scores over time, traders can identify trends and patterns to inform their future trading strategies.
A blended approach
The most comprehensive approach is to combine elements of each analysis style to gain a holistic understanding of the stocks you plan to invest in or trade and implement the correct strategy based on the prevailing market conditions and other relevant factors.
Complementing fundamental and technical analysis with sentiment analysis can reinforce certain views, which traders and investors can express through easy-to-use trading platforms like Clarity, by Investec.